Hello,
In this thread, I want to propose a LIP for the roadmap objective Introduce token standards. The proposal’s contribution is to define a non-fungible token module to be used in the Lisk ecosystem.
I’m looking forward to your feedback.
Here is a complete LIP draft:
LIP:
Title: Introduce NFT module
Author: Maxime Gagnebin <maxime.gagnebin@lightcurve.io>
Type: Standards Track
Created: <YYYY-MM-DD>
Updated: <YYYY-MM-DD>
Requires: Introduce Interoperability module
Discussions-To: https://research.lisk.com/t/introduce-nft-module
Abstract
This topic introduces an NFT (non-fungible token) module to be used in the Lisk ecosystem for creating, destroying NFTs, and transferring them in the ecosystem.
NFTs are uniquely identified assets.
They can be transferred similarly to fungible tokens, but their unique identifiers can never be modified.
In this module, NFTs also carry a list of attributes that are used to store information specific to the NFT.
Copyright
This LIP is licensed under the Creative Commons Zero 1.0 Universal.
Motivation
NFTs are very common in the blockchain space and have uses in a wide range of applications.
This can go from being the virtual representation of a real world object (art, fashion, event tickets …) to purely virtual collectibles (crypto kitties, …).
Therefore, providing a unified module to handle, transfer and modify NFTs is a necessity for the Lisk ecosystem.
The module presented here contains all the basic features that are needed to incorporate NFTs in a blockchain ecosystem without being restrictive on the way NFTs will be used by custom modules and applications.
Rationale
Technical Glossary
- Native chain: with regards to an NFT, this is the chain where the NFT was created.
- Native NFT: with regards to a chain, all NFTs created on this chain.
- Foreign chain: with regards to an NFT, all chains other than the native chain.
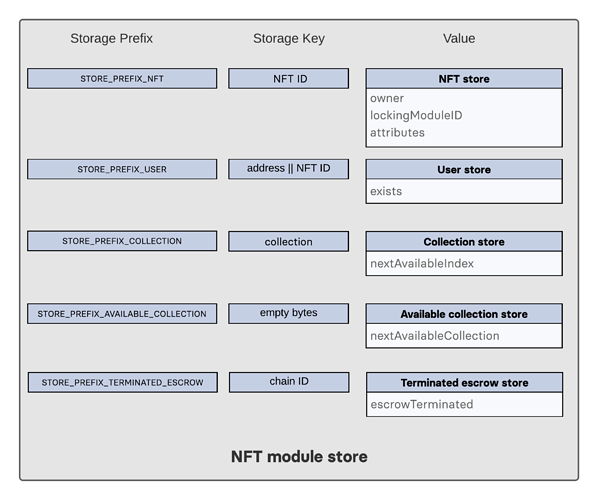
NFT Module Store
Figure 1: The NFT module store is divided into 5 substores. All NFTs held by users are stored sequentially in the user substore with keys given by the user address and the NFT ID.
NFT Store
The NFT store contains entries for all NFTs present on the chain, as well as entries for all native NFTs that have been sent cross-chain.
Each entry contains three properties, the owner, the locking module ID and the attributes of the NFT. The owner can either be a 20 bytes user address, or a 4 bytes serialization of a chain ID.
In the latter case, the token is a native token that has been sent cross-chain and is escrowed.
The locking module ID stores the information regarding the locking status of the NFT.
If the NFT is unlocked, this property will have value NFT_NOT_LOCKED, whereas if the NFT is locked, this property will store the ID of the locking module.
Lastly, the NFT stores an attribute property which can be used by custom applications to store information about the NFT, or modify interactions with the NFT.
User Substore
In the proposed solution, all NFTs associated with a given address are stored sequentially in the user substore part of the state.
In this way, getting all NFTs of a given account can be done efficiently.
This is in contrast to specifications (like ERC 721 without optional extensions) where the NFT owner is only stored as one of the NFTs properties.
We think that this feature is useful in an account based blockchain ecosystem and the user substore is designed accordingly.
NFT Identifier
To identify NFTs in the Lisk ecosystem, we introduce the NFT ID in this proposal.
An NFT ID will be unique in the ecosystem.
It is built from 3 integers: the chain ID of the chain creating the token, a collection integer chosen when the token is created and an index which is automatically assigned to the new NFT.
This allows chains to define multiple sets of NFTs, each identified by their respective collection.
Each collection can then easily have its own attribute schema and custom logic.
For example, an art NFT exchange could have a different collection per artist.
The index being then the unique integer associated with each art piece of this artist.
Cross-chain NFT Transfer
To allow cross-chain transfers of NFTs, we define a specific command which makes use of the Interoperability module and creates a cross-chain message with the relevant information.
When sending NFTs cross-chain, it is crucial that every chain can correctly escrow its native tokens sent to other chains.
In this way, a native NFT can never be created by a foreign chain and sent across the ecosystem.
When receiving non-native NFTs on a chain, users can query this NFT’s native chain to make sure that the NFT is properly escrowed.
Transfer To and From the Native Chain
These specifications only allow NFTs to be transferred to and from their native chain.
In particular, this means that a token created on chain A cannot be transferred directly from chain B to chain C.
This is required to allow the native chain to maintain correctly escrowed NFTs.
Attributes
Each NFT is stored with an attribute property.
This property is a byte sequence that is not deserialized by the NFT module.
Each custom module using an NFT collection should define schemas to serialize and deserialize the attribute property of NFTs of their collection.
When an NFT is sent to another chain, the attributes property of the NFT can be modified according to specifications set on the receiving chain.
For this reason, custom modules specifying an NFT collection must also implement the behavior to adopt when an NFT is returned with a modified attributes property.
This custom behavior will compare the returned attributes with the ones stored with the escrowed NFT.
If the returned NFT has an empty attribute, the native chain will restore the attributes as stored,
this can be used to save on cross-chain messages size when returning non-modified NFTs to their native chains.
Protocol Logic for Other Modules
The NFT module provides the following functions to modify the NFT state.
Any other modules should use those functions to modify the NFT state.
The NFT state should never be modified from outside the module without using one of the provided functions as this could result in unexpected behavior and could cause an improper state transition.
create
This function is used to create a new NFT.
The NFT will always be native to the chain creating it.
The index of the created NFT will be the next available index, as specified by the max index corresponding to the collection.
destroy
This function is used to destroy NFTs.
The NFT will be removed from the NFT store and cannot be retrieved.
The use of this function is limited to destroying native NFTs.
transfer
This function is used to transfer ownership of NFTs within one chain.
transferCrossChain
This function is used to transfer ownership of NFTs across chains in the Lisk ecosystem.
lock
This function is used to lock an NFT to a module ID.
A locked NFT cannot be transferred (within the chain or across chains).
This can be useful, for example, when the NFT is used as a deposit for a service.
A module ID is specified when locking the NFT and this ID has to be specified when unlocking the NFT.
This avoids NFTs being accidentally locked and unlocked by different modules.
unlock
This function is used to unlock an NFT that was locked to a module ID.
setAttributes
This function is used to modify the attributes of NFTs.
Each custom module can define the rules surrounding modifying NFT attributes and should call this function.
This function will be executed even if the NFT is locked.
recover
This function should only be called by the Interoperability module to trigger the recovery of NFTs escrowed to terminated chains.
Specification
Constants and Notations
The following constants are used throughout the document
| Name | Type | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Interoperability Constants | ||
MIN_RETURN_FEE |
uint64 | 1000 |
| NFT Module Constants | ||
MODULE_ID_NFT |
uint32 | TBD |
COMMAND_ID_TRANSFER |
uint32 | 0 |
COMMAND_ID_CROSS_CHAIN_TRANSFER |
uint32 | 1 |
CROSS_CHAIN_COMMAND_ID_TRANSFER |
uint32 | 0 |
CHAIN_ID_ALIAS_NATIVE |
uint32 | 0 |
NFT_NOT_LOCKED |
uint32 | MODULE_ID_NFT |
MAX_BYTE_LENGTH_ATTRIBUTES |
uint32 | 9 * 1024 |
CCM_STATUS_OK |
uint32 | 0 |
CCM_STATUS_NFT_NOT_SUPPORTED |
uint32 | 64 |
CCM_STATUS_NFT_PROTOCOL_VIOLATION |
uint32 | 65 |
| Store Constants | ||
STORE_PREFIX_NFT |
bytes | 0x00 00 |
STORE_PREFIX_USER |
bytes | 0x80 00 |
STORE_PREFIX_COLLECTION |
bytes | 0xc0 00 |
STORE_PREFIX_AVAILABLE_COLLECTION |
bytes | 0xd0 00 |
STORE_PREFIX_TERMINATED_ESCROW |
bytes | 0xe0 00 |
STORE_KEY_LENGTH_NFT |
uint32 | 16 |
| General Constants | ||
EMPTY_BYTES |
bytes | “” |
ADDRESS_LENGTH |
uint32 | 20 |
uint32be
uint32be(x) returns the big endian uint32 serialization of an integer x, with 0 <= x <2^32.
This serialization is always 4 bytes long.
uint64be
uint64be(x) returns the big endian uint64 serialization of an integer x, with 0 <= x < 2^64.
This serialization is always 8 bytes long.
length
In this LIP, length(byteSequence) returns the length in bytes of byteSequence.
Functions from Other Modules
Calling a function fct from the Interoperability module is represented by interoperability.fct(required inputs).
NFT Module Store
The store keys and schemas for value serialization of the NFT store are set as follows:
NFT Substore
- The store prefix is set to
STORE_PREFIX_NFT. - Each store key is an NFT ID:
uint32be(chainID)||uint32be(collection)||uint64be(index). - Each store value is the serialization of an object following
NFTStoreSchema.NFTStoreSchema = { "type": "object", "required": [ "owner", "lockingModuleID", "attributes" ], "properties": { "owner": { "dataType": "bytes", "fieldNumber": 1 }, "lockingModuleID": { "dataType": "uint32", "fieldNumber": 2 }, "attributes": { "dataType": "bytes", "fieldNumber": 3 } } }
User Substore
- The store prefix is set to
STORE_PREFIX_USER. - Each store key is a 20-byte address and an NFT ID:
address||uint32be(chainID)||uint32be(collection)||uint64be(index). - Each store value is the serialization of an object following
userStoreSchema.userStoreSchema = { "type": "object", "required": ["exists"], "properties": { "exists": { "dataType": "boolean", "fieldNumber": 1 } } }
Collection Substore
- The store prefix is set to
STORE_PREFIX_COLLECTION. - Each store key is a collection:
uint32be(collection). - Each store value is the serialization of an object following
collectionStoreSchema.collectionStoreSchema = { "type": "object", "required": ["nextAvailableIndex"], "properties": { "nextAvailableIndex": { "dataType": "uint64", "fieldNumber": 1 } } }
Available Collection Substore
- The store prefix is set to
STORE_PREFIX_AVAILABLE_COLLECTION. - Each store key is the empty bytes.
- Each store value is the serialization of an object following
availableCollectionStoreSchema.availableCollectionStoreSchema = { "type": "object", "required": ["nextAvailableCollection"], "properties": { "nextAvailableCollection": { "dataType": "uint32", "fieldNumber": 1 } } }
Terminated Escrow Substore
- The store prefix is set to
STORE_PREFIX_TERMINATED_ESCROW. - Each store key is a chain ID:
uint32be(chainID). - Each store value is the serialization of an object following
terminatedEscrowStoreSchema.terminatedEscrowStoreSchema = { "type": "object", "required": ["escrowTerminated"], "properties": { "escrowTerminated": { "dataType": "boolean", "fieldNumber": 1 } } }
Store Notation
For the rest of this proposal:
- Let
NFTStore(nftID)be the NFT store entry with store prefixSTORE_PREFIX_NFTand store key
uint32be(nftID.chainID)||uint32be(nftID.collection)||uint64be(nftID.index). - Let
userStore(address, nftID)be the user substore entry with store keyaddress||uint32be(nftID.chainID)||uint32be(nftID.collection)||uint64be(nftID.index). - Let
collectionStore(collection)be the collection substore entry with store keyuint32be(collection). - Let
terminatedStore(chainID)be theescrowTerminatedproperty of the terminated escrow substore entry with store keyuint32be(chainID).
If the store entry does not exist, the function returnsFalse. - Let
nextAvailableCollectionbe thenextAvailableCollectionproperty of the entry of the available collection substore.
NFT Identification
All NFTs in the ecosystem are identified by the three values chainID, collection and index.
-
chainIDis always the chain ID of the chain that created the NFT -
collectionis an integer specified at NFT creation, -
indexis assigned at NFT creation to the next available index in the collection.
In this LIP, the NFT identifier is written as a dictionary of 3 elements {"chainID": chainID, "collection": collection, "index": index}.
This is for example used in all input formats for the module’s exposed logics.
This allows the exposed logic interfaces to be simple and uniform.
This choice follows a potential way how the module could be implemented in JavaScript, the same behavior could be implemented with a named tuple in Python.
NFT ID and Native NFT
NFTs on their native chain are identified by the three values {"chainID": CHAIN_ID_ALIAS_NATIVE, "collection": collection, "index": index}.
The same NFT in other chains would be identified by the three values {"chainID": nativeChainID, "collection": collection, "index": index},
nativeChainID being the chain ID of the chain where the NFT was created.
Supported NFTs
The NFT module contains a function used when receiving cross-chain NFT transfers to assert the support for non-native NFTs.
It should return a boolean, depending on the configuration of the NFT module.
For the rest of this LIP, this function is written NFTSupported(nftID).
Internal Functions
createNFTEntry
createNFTEntry(nftID, address, moduleID, givenAttributes):
create a store entry with
storePrefix = STORE_PREFIX_NFT
storeKey = uint32be(nftID.chainID)
|| uint32be(nftID.collection)
|| uint64be(nftID.index)
storeValue = {
"owner": address,
"lockingModuleID": moduleID,
"attributes": givenAttributes
} serialized using NFTStoreSchema
deleteNFTEntry
deleteNFTEntry(nftID):
delete the store entry with
storePrefix = STORE_PREFIX_NFT
storeKey = uint32be(nftID.chainID)
|| uint32be(nftID.collection)
|| uint64be(nftID.index)
createUserEntry
createUserEntry(address, nftID):
create an store entry with
storePrefix = STORE_PREFIX_USER
storeKey = address
|| uint32be(nftID.chainID)
|| uint32be(nftID.collection)
|| uint64be(nftID.index)
storeValue = {"exists": True} serialized using userStoreSchema
deleteUserEntry
deleteUserEntry(address, nftID):
delete the store entry with
storePrefix = STORE_PREFIX_USER
storeKey = address
|| uint32be(nftID.chainID)
|| uint32be(nftID.collection)
|| uint64be(nftID.index)
terminateEscrow
terminateEscrow(chainID):
create the store entry with
storePrefix = STORE_PREFIX_TERMINATED_ESCROW.
storeKey = uint32be(chainID)
storeValue = {"escrowTerminated": True} serialized according to terminatedEscrowStoreSchema
canonicalNFTID
canonicalNFTID(nftID):
if nftID.chainID == interoperability.getOwnChainAccount().ID
return {"chainID": CHAIN_ID_ALIAS_NATIVE, "collection": nftID.collection, "index": nftID.index}
else:
return nftID
This function will return the input nftID in the case interoperabiliby.getOwnChainAccount() cannot be called.
NFT Attributes
For all NFT collections, native chains must implement the function
getNewAttributes(collection, storedAttributes, receivedAttributes) which is used whenever an NFT from this collection is received from another chain.
The function getNewAttributes must always return a byte array of length at most MAX_BYTE_LENGTH_ATTRIBUTES bytes.
For all values of collection and storedAttributes,
this function must be defined as getNewAttributes(collection, storedAttributes, EMPTY_BYTES) = storedAttributes.
This function’s default behavior is to always overwriting the received attributes with the ones in the NFT substore:
defaultGetNewAttributes(collection, storedAttributes, receivedAttributes):
return storedAttributes
NFTs in Genesis Blocks
The genesis block of a chain can have a non-empty NFT store. The distribution of NFTs at genesis is left to sidechain developers and must only follow few restrictions:
- No escrow entries (entries with store prefix
ESCROW_STORE_PREFIX) should exist in the genesis block. - Only NFTs with
chainID == CHAIN_ID_ALIAS_NATIVEexist in the genesis block. They must all have a 20 byte owner and the corresponding entry in the user substore must exist (entry with store key beingowner||uint32be(chainID)||uint23be(collection)||uint64be(index)). - For all collections, the maximal index of all NFTs of this collection, over all existing NFT entries, must be strictly smaller than
collectionStore(collection).nextAvailableIndex. -
nextAvailableCollection > collectionfor allcollectionsuch thatcollectionStore(collection)exists.
Commands
The module provides the following commands to modify the NFT store.
NFT Transfer
Transactions executing this command have:
moduleID = NFT_MODULE_IDcommandID = COMMAND_ID_TRANSFER
Parameters Schema
The params property of an NFT transfer transaction follows the schema NFTTransferParams.
NFTTransferParams = {
"type": "object",
"required": [
"nftID",
"recipientAddress"
],
"properties": {
"nftID": {
"type": object,
"fieldNumber": 1,
"required": [
"chainID",
"collection",
"index"
],
"properties": {
"chainID": {
"dataType": "uint32",
"fieldNumber": 1
},
"collection": {
"dataType": "uint32",
"fieldNumber": 2
},
"index": {
"dataType": "uint64",
"fieldNumber": 3
}
}
},
"recipientAddress": {
"dataType": "bytes",
"fieldNumber": 2
}
}
}
Parameters Validity
The params property of an NFT transfer transaction is valid if:
-
recipientAddressmust be a byte array of lengthADDRESS_LENGTH.
Execution
When executing this command, the following is done:
derive senderAddress from trs.senderPublicKey
let nftID as given in trs.params
if NFTStore(nftID).lockingModuleID != NFT_NOT_LOCKED:
execution fails
if NFTStore(nftID).owner != senderAddress:
execution fails
deleteUserEntry(senderAddress, nftID)
createUserEntry(recipientAddress, nftID)
NFTStore(nftID).owner = recipientAddress
Cross-chain NFT Transfer
Transactions executing this command have:
moduleID = NFT_MODULE_IDcommandID = COMMAND_ID_CROSS_CHAIN_TRANSFER
Parameters Schema
The params property of a cross-chain NFT transfer transaction follows the schema crossChainTransferParams.
crossChainTransferParams = {
"type": "object",
"required": [
"nftID",
"receivingChainID",
"recipientAddress",
"messageFee"
],
"properties": {
"nftID": {
"type": object,
"fieldNumber": 1,
"required": [
"chainID",
"collection",
"index"
],
"properties": {
"chainID": {
"dataType": "uint32",
"fieldNumber": 1
},
"collection": {
"dataType": "uint32",
"fieldNumber": 2
},
"index": {
"dataType": "uint64",
"fieldNumber": 3
}
}
},
"receivingChainID": {
"dataType": "uint32",
"fieldNumber": 2
},
"recipientAddress": {
"dataType": "bytes",
"fieldNumber": 3
},
"messageFee": {
"dataType": "uint64",
"fieldNumber": 4
}
}
}
Parameters Validity
The params property of a cross-chain NFT transfer transaction is valid if:
-
recipientAddressis a byte array of lengthADDRESS_LENGTH, -
tokenID.chainIDis eitherCHAIN_ID_ALIAS_NATIVEorreceivingChainID,
Execution
When executing a cross-chain NFT transfer transaction trs, the following is done:
- Derive
senderAddressfromtrs.senderPublicKey. - Execute the same logic as the function
timestamp = timestamp of the block including the execution of this command transferCrossChain(timestamp, senderAddress, trs.params.receivingChainID, trs.params.recipientAddress, trs.params.nftID, trs.params.messageFee)
Executing Cross-chain Messages
Cross-chain NFT Transfer Message
Cross-chain messages executing this cross-chain command have:
-
moduleID = NFT_MODULE_ID, commandID = CROSS_CHAIN_COMMAND_ID_TRANSFER
Message Parameters Schema
The params property of cross-chain NFT transfers follows the crossChainTransferMessageParams schema.
crossChainTransferMessageParams = {
"type": "object",
"required": [
"nftID",
"senderAddress"
"recipientAddress",
"attributes"
],
"properties": {
"nftID": {
"type": object,
"fieldNumber": 1,
"required": [
"chainID",
"collection",
"index"
],
"properties": {
"chainID": {
"dataType": "uint32",
"fieldNumber": 1
},
"collection": {
"dataType": "uint32",
"fieldNumber": 2
},
"index": {
"dataType": "uint64",
"fieldNumber": 3
}
}
},
"senderAddress": {
"dataType": "bytes",
"fieldNumber": 2
},
"recipientAddress": {
"dataType": "bytes",
"fieldNumber": 3
},
"attributes": {
"dataType": "bytes",
"fieldNumber": 4
}
}
}
Execution
When executing a cross-chain NFT transfer message CCM, the logic below is followed.
nftID = CCM.params.nftID
chainID = nftID.chainID
sendingChainID = CCM.sendingChainID
senderAddress = CCM.params.senderAddress
recipientAddress = CCM.params.recipientAddress
receivedAttributes = CCM.params.attributes
ownChainID = interoperability.getOwnChainAccount().ID
if (chainID not in [ownChainID, sendingChainID]
or length(senderAddress) != ADDRESS_LENGTH
or length(recipientAddress) != ADDRESS_LENGTH
or length(receivedAttributes) > MAX_BYTE_LENGTH_ATTRIBUTES
or (chainID == ownChainID
and NFTStore(nftID).owner != uint32(sendingChainID))
or (chainID == sendingChainID
and NFTStore(nftID) exists)):
if (CCM.fee >= MIN_RETURN_FEE * length(CCM)
and CCM.status == CCM_STATUS_OK):
interoperability.error(CCM, CCM_STATUS_NFT_PROTOCOL_VIOLATION)
terminateEscrow(sendingChainID)
stop CCM execution
if chainID == ownChainID:
oldAttributes = NFTStore(nftID).attributes
if CCM.status == CCM_STATUS_OK:
newAttributes = getNewAttributes(nftID.collection,
oldAttributes,
receivedAttributes)
newRecipientAddress = recipientAddress
else:
newAttributes = oldAttributes
newRecipientAddress = senderAddress
nftID = canonicalNFTID(nftID)
NFTStore(nftID).owner = newRecipienAddress
NFTStore(nftID).attributes = newAttributes
createUserEntry(newRecipientAddress, nftID)
else: # chainID == sendingChainID
if NFTSupported(nftID) == FALSE:
if (CCM.fee >= MIN_RETURN_FEE * length(CCM)
and CCM.status == CCM_STATUS_OK):
interoperability.error(CCM, CCM_STATUS_NFT_NOT_SUPPORTED)
stop CCM execution
if CCM.status == CCM_STATUS_OK:
createNFTEntry(nftID,
recipientAddress,
receivedAttributes)
createUserEntry(recipientAddress, nftID)
else:
createNFTEntry(nftID,
senderAddress,
receivedAttributes)
createUserEntry(senderAddress, nftID)
Protocol Logic for Other Modules
getAttributes
This function returns the attributes of an NFT.
getAttributes(address, nftID):
nftID = canonicalNFTID(nftID)
if NFTStore(nftID) exists:
return NFTStore(nftID).attributes
else:
return entry does not exist
getLockingModuleID
This function returns the locking status of an NFT.
getLockingModuleID(nftID):
nftID = canonicalNFTID(nftID)
if NFTStore(nftID) exists:
return NFTStore(nftID).lockingModuleID
else:
return entry does not exist
getNFTowner
This function returns the owner of an NFT.
getNFTowner(nftID):
nftID = canonicalNFTID(nftID)
if NFTStore(nftID) exists:
return NFTStore(nftID).owner
else:
return entry does not exist
isTerminated
This function returns the escrow status of a chain.
isTerminated(chainID):
if terminatedStore(chainID) == True:
return True
else:
return False
getNextAvailableIndex
This function returns the max index of a collection.
getNextAvailableIndex(collection):
if collectionStore(collection) does not exist:
return collection does not exist
return collectionStore(collection).nextAvailableIndex
getNextAvailableCollection
This function returns the next available collection.
getNextAvailableCollection():
return nextAvailableCollection
create
This function creates an NFT.
create(address, collection, attributes):
if (length(attributes) > MAX_BYTE_LENGTH_ATTRIBUTES bytes
or collectionStore(collection) does not exist):
create fails
index = collectionStore(collection).nextAvailableIndex
nftID = {"chainID": CHAIN_ID_ALIAS_NATIVE,
"collection": collection,
"index": index}
createNFTEntry(nftID, address, attributes)
createUserEntry(address, nftID)
collectionStore(collection).nextAvailableIndex += 1
destroy
This function destroys an NFT.
destroy(nftID):
nftID = canonicalNFTID(nftID)
if (nftID.chainID != CHAIN_ID_ALIAS_NATIVE
or NFTStore(nftID) does not exist):
destroy fails
address = NFTStore(nftID).owner
deleteNFTEntry(nftID)
deleteUserEntry(address, nftID)
initializeCollection
This function creates a new collection substore entry.
initializeCollection(collection):
if collectionStore(collection) exists:
initializeCollection fails
create an entry in the collection substore with
storeKey = uint32be(collection)
storeValue = {"nextAvailableIndex": 0) serialized using collectionStoreSchema
if collection >= nextAvailableCollection:
nextAvailableCollection = collection + 1
return collection
transfer
This function transfers ownership of NFTs within one chain.
transfer(senderAddress, recipientAddress, nftID):
nftID = canonicalNFTID(nftID)
if (NFTStore(nftID).lockingModuleID != NFT_NOT_LOCKED
or NFTStore(nftID).owner != senderAddress):
transfer fails
deleteUserEntry(senderAddress, nftID)
createUserEntry(recipientAddress, nftID)
NFTStore(nftID).owner = recipientAddress
transferCrossChain
This function transfers ownership of NFTs across chains in the Lisk ecosystem.
transferCrossChain(timestamp,
senderAddress,
receivingChainID,
recipientAddress,
nftID,
messageFee,
includeAttributes):
nftID = canonicalNFTID(nftID)
chainID = nftID.chainID
if (chainID not in [CHAIN_ID_ALIAS_NATIVE, receivingChainID]
or length(senderAddress) != ADDRESS_LENGTH
or length(recipientAddress) != ADDRESS_LENGTH
or NFTStore(nftID).owner != senderAddress
or NFTStore(nftID).lockingModuleID != NFT_NOT_LOCKED
or (terminatedStore(sendingChainID) == True
and chainID == CHAIN_ID_ALIAS_NATIVE)):
transferCrossChain fails
if includeAttributes == True:
attributes = NFTStore(nftID).attributes
else:
attributes = EMPTY_BYTES
deleteUserEntry(address, nftID)
if chainID == CHAIN_ID_ALIAS_NATIVE:
NFTStore(nftID).owner = uint32be(receivingChainID)
nftID.chainID = interoperability.getOwnChainAccount().ID
else:
deleteNFTEntry(nftID)
messageParams = {
"nftID": nftID,
"senderAddress": senderAddress,
"recipientAddress": recipientAddress
"attributes": attributes,
}
serializedParams = serialization of messageParams following
crossChainTransferMessageParams schema
interoperability.send(timestamp,
NFT_MODULE_ID,
CROSS_CHAIN_COMMAND_ID_TRANSFER,
receivingChainID,
messageFee,
senderAddress,
serializedParams)
lock
This function locks an NFT to a given module ID.
lock(moduleID, nftID):
nftID = canonicalNFTID(nftID)
if NFTStore(nftID).lockingModuleID != NFT_NOT_LOCKED:
lock fails
NFTStore(nftID).lockingModuleID = moduleID
unlock
This function unlocks an NFT that was locked to a module ID.
unlock(moduleID, nftID):
nftID = canonicalNFTID(nftID)
if NFTStore(nftID).lockingModuleID != moduleID:
unlock fails
NFTStore(nftID).lockingModuleID = NFT_NOT_LOCKED
setAttributes
This function modifies the attributes of NFTs.
setAttributes(newAttributes, nftID):
nftID = canonicalNFTID(nftID)
if (NFTStore(nftID) does not exist
or length(newAttributes) > MAX_BYTE_LENGTH_ATTRIBUTES):
setAttributes fails
NFTStore(nftID).attributes = newAttributes
recover
This function should only be called by the interoperability module.
It recovers NFTs escrowed to terminated chains.
recover(terminatedChainID, moduleID, storePrefix, storeKey, storeValue):
if (storePrefix != STORE_PREFIX_NFT:
or length(storeKey) != STORE_KEY_LENGTH_NFT):
recover fails
chainID = first 4 bytes of storeKey deserialized as uint32be
collection = bytes 5 to 8 of storeKey deserialized as uint32be
index = last 8 bytes of storeKey deserialized as uint64be
nftID = {"chainID": chainID, "collection": collection, "index": index}
if (chainID != interoperability.getOwnChainAccount().ID
or NFTStore(nftID).owner != uint32be(terminatedChainID)
or storeValue does not follow nftStoreSchema):
recover fails
nftValue = storeValue deserialized according to nftStoreSchema
if length(nftValue.owner) != ADDRESS_LENGTH:
recover fails
NFTStore(nftID).owner = nftValue.owner
storedAttributes = NFTStore(nftID).attributes
newAttributes = nftValue.attributes
NFTStore(nftID).attributes = getNewAttributes(collection, storedAttributes, newAttributes)
Endpoints for Off-Chain Services
TBA
Backwards Compatibility
Chains adding support for the NFT module specified in this document need to do so with a hard fork. This proposal does not imply a fork for the Lisk mainchain.
Reference Implementation
TBA